Blood Pressure Chart by Age: Is Your Number Normal? (Free Guide)

Medical Disclaimer: The content in this article is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition
The Anxiety of the “Cuff Squeeze”
You know the feeling well. You are sitting on the crinkly paper of the exam table. The nurse wraps the Velcro cuff around your arm. As it tightens, squeezing harder and harder, you hold your breath. You stare at the digital screen, waiting for the numbers to pop up.
Beep. The numbers flash: 138/88. Your heart sinks a little. Is that good? Is it bad? Last year it was lower. Does this mean you have heart disease?
If you feel this anxiety, known as “White Coat Syndrome,” it is OK! You are not alone. Millions of people experience a spike in blood pressure simply because they are nervous about the result. But fear often comes from the unknown.
In this guide, we aren’t just giving you a chart. We are going to explain exactly why these numbers change as you age, so you can stop worrying and start understanding your body.
What Do the Numbers Actually Mean? (The Garden Hose Analogy)

Before we look at the chart, we need to demystify the two numbers on the screen. Doctors throw around terms like “systolic” and “diastolic,” but what is happening inside your veins?
Imagine your blood vessels are like garden hoses in your backyard.
1. Systolic (The Top Number) = The “Water On” Pressure
Think of this as the moment you turn the faucet on full blast. Water rushes through the hose with force.
- Biologically: This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pushes blood out to your body.
2. Diastolic (The Bottom Number) = The “Resting” Pressure
Now, imagine you turn the faucet off for a split second between sprays. There is still water in the hose, but the pressure is lower.
- Biologically: This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats to refill with blood.
Why Both Matter:
If the pressure is too high when the water is rushing (Systolic), the hose can burst. If the pressure remains too high even when the water is off (Diastolic), the hose never gets a break and wears out faster.
The Ultimate Blood Pressure Chart by Age
While the general “Gold Standard” for a healthy heart is often cited as 120/80 mmHg, the reality is more nuanced. As we age, our bodies change, and “normal” can look slightly different.
Use this chart as your primary reference guide.
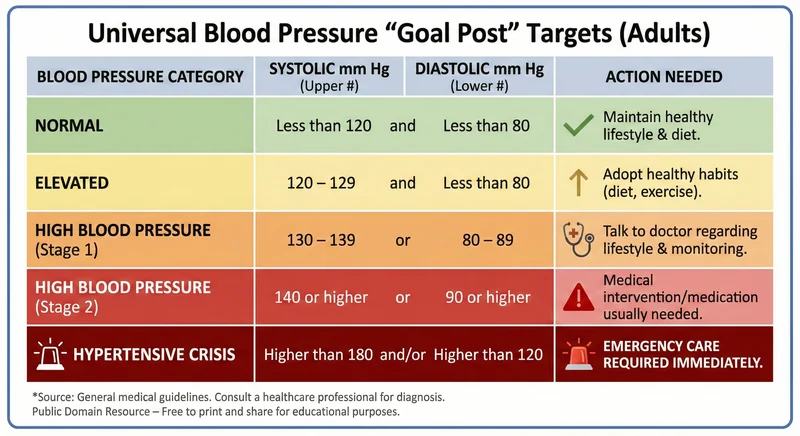
Blood Pressure Categories (General Adults)
| Category | Systolic (Top Number) | and/or | Diastolic (Bottom Number) | Action Required |
| 🟢Normal | Less than 120 | and | Less than 80 | Healthy! Keep up good habits. |
| 🟡Elevated | 120 – 129 | and | Less than 80 | Yellow Light. Start lifestyle changes (diet/exercise). |
| 🟠High (Stage 1) | 130 – 139 | or | 80 – 89 | Talk to Doctor. Monitor closely. |
| 🔴High (Stage 2) | 140 or higher | or | 90 or higher | Medical Alert. Medical intervention is usually needed. |
| 🚨Hypertensive Crisis | Higher than 180 | and/or | Higher than 120 | EMERGENCY. Call 911. Emergency care required immediately. |
(Source: Guidelines from the American Heart Association)
Deep Dive: Decoding the Categories
What is actually happening to your body in these stages?
- Normal (The Smooth Flow): When your numbers are under 120/80, your blood is flowing smoothly. There is no friction damaging the delicate inner lining of your arteries (the endothelium). Your risk of stroke or heart attack is at its lowest.
- Elevated (The “Yellow Light”): Think of this as a warning shot. Your system is starting to stiffen. You don’t need medication yet, but you have a critical window of opportunity. Studies show that acting here—by cutting salt or walking more—can prevent you from ever needing pills.
- Stage 1 & 2 (The Danger Zone): At this level, the “water pressure” in your hose is so high that it is causing micro-tears in the walls. Your body tries to patch these tears with cholesterol (plaque), which narrows the arteries even more. This is why doctors prescribe medication—to lower the pressure before permanent damage occurs.
Average Blood Pressure by Age & Gender
This chart reflects statistical averages. Note how numbers creep up with age. If a reader is in the “Average” range for a 60-year-old (e.g., 134/84), they are technically in the High BP (Stage 1) category and should look into home remedies or medical advice to lower it.
| Age Group | Men (Average) | Women (Average) | Insight |
| 21 – 25 | 120 / 79 | 115 / 75 | Focusing on low sodium is crucial. |
| 26 – 30 | 121 / 80 | 115 / 75 | Men tend to see a slight rise earlier. |
| 31 – 35 | 123 / 82 | 116 / 76 | Stress and diet begin to play a role. |
| 36 – 40 | 125 / 83 | 120 / 78 | Monitoring becomes important here. |
| 41 – 45 | 127 / 84 | 122 / 79 | Mid-life metabolic changes occur. |
| 46 – 50 | 129 / 85 | 128 / 82 | Women’s BP often rises post-menopause. |
| 51 – 55 | 131 / 86 | 132 / 83 | Arteries naturally begin to stiffen. |
| 56 – 60 | 133 / 87 | 134 / 84 | Women may average higher than men here. |
| 61 – 65 | 135 / 88 | 136 / 85 | Focus on low sodium is crucial. |
| Over 65 | 136 / 87 | 137 / 85 | Typically, the optimal baseline. |
Note: You will notice that after age 50, women often have slightly higher blood pressure than men. This is largely due to hormonal changes (drop in estrogen) during menopause, which offers less protection to the heart.
Understanding Average Blood Pressure by Age Table
The table represents what is COMMON among people, but it is NOT HEALTHY.
The Difference Between “Average” and “Healthy.”
- Average (Statistical): This simply means what usually happens to people. In many populations, people eat processed foods, don’t exercise enough, and experience stress. Therefore, the “average” person gets higher blood pressure as they age.
- Healthy (Optimal): This is what should happen for your body to stay safe. Medical guidelines do not raise the safe limit just because you are older.
- Example: Just because the “average” 60-year-old has a BP of 134/87, that doesn’t mean it’s safe. That reading is still considered Stage 1 Hypertension and increases the risk of stroke and heart attack.
The “Silent Acceptance” Trap
Many people think, “Oh, I’m 55, so it’s normal for my pressure to be a bit high.” This is a dangerous myth. While it is harder to keep BP down as we age, the target remains the same: below 120/80 is the gold standard, and definitely below 130/80 to minimize risks.
While it is a biological fact that our blood vessels stiffen with age, causing pressure to rise, we should not accept high numbers as ‘normal.’ The rising average in the charts represents a rising risk of heart disease. This is exactly why home remedies, diet, and lifestyle changes become more important the older we get, not less.
Real-Life Scenarios: Does Age Matter?
To understand how age affects these targets, let’s look at two hypothetical patients.
Meet Alex (Age 20):
- Reading: 135/85 mmHg.
- Verdict: High.
- The Why: For a 20-year-old with young, elastic arteries, this reading is alarming. It suggests a premature health issue or poor lifestyle habits that need immediate correction to prevent early heart disease.
Meet Linda (Age 65):
- Reading: 135/85 mmHg.
- Verdict: Acceptable (depending on the doctor).
- The Why: Linda’s arteries have naturally stiffened over 65 years. While 120/80 is still the ideal goal, forcing her pressure too low with heavy medication might cause dizziness or falls. Her doctor might be satisfied with a stable 135 systolic to balance heart health with safety.
Why Does Blood Pressure Change as We Age

One of the most common questions patients ask is: “I haven’t changed my diet or my exercise routine. Why is my blood pressure going up?”
It can feel frustrating, like your body is betraying you. But it is important to understand that this is a natural biological process. It is not necessarily your fault.
Here is the deep dive into why your numbers shift as you get older.
1. The “Rubber Band” Effect (Arterial Stiffness)
To understand aging, think of a brand-new rubber band. It is stretchy and flexible. When you pull it, it snaps back easily.
- Young Arteries: When you are in your 20s, your arteries act like that new rubber band. When the heart pumps blood, the arteries expand to handle the flow, keeping pressure low.
- Older Arteries: As decades pass, the walls of your arteries slowly lose that stretchiness. They become stiffer, more like a rigid pipe than a flexible tube. This condition is called arteriosclerosis.
Because the “pipe” won’t expand, your heart has to pump with more force to get the blood through. This extra force shows up as a higher top number (Systolic pressure).
2. The Hormonal Shift (Menopause)
For women, age brings a specific game-changer: Menopause.
- The Shield: Before menopause, a hormone called estrogen helps protect women’s blood vessels, keeping them flexible and relaxed.
- The Shift: After menopause (usually around age 50+), estrogen levels drop significantly. Without this natural protection, blood pressure often rises sharply, sometimes catching up to or even surpassing that of men of the same age.
3. The “Filter” Factor (Kidney Function)
Your kidneys are the unsung heroes of blood pressure control. They act as the body’s filtration system, deciding how much salt and water to keep and how much to pee out.
- The Mechanism: As we age, our kidneys naturally filter blood a little slower. If they don’t flush out salt as efficiently as they used to, your body holds onto extra water.
- The Result: More water in your system means more volume in your blood vessels. Think of it like overfilling a water balloon—the pressure inside goes up.
How to Measure Accurate Numbers at Home
Did you know that readings taken at a doctor’s office are often inaccurate? Between the rush of the appointment and the anxiety of the environment, your numbers can spike falsely.
Home monitoring is the “Gold Standard” for managing your health. But you have to do it exactly right. A small mistake, like crossing your legs, can skew the result by 2 to 8 points.
Follow this 7-Step “Perfect Reading” Ritual to ensure your numbers are real.
Step 1: The 30-Minute Rule
Preparation starts half an hour before you even touch the cuff. Avoid these three triggers, as they act as temporary stimulants that spike pressure:
- No Caffeine: Coffee constricts blood vessels.
- No Smoking: Nicotine raises your heart rate instantly.
- No Exercise: Even a brisk walk raises pressure temporarily (which is good exercise, but bad for a resting reading).
Step 2: The Empty Bladder Rule
This is the most common mistake. A full bladder puts pressure on your kidneys and blood vessels.
- The Impact: Measuring with a full bladder can add 10 to 15 points to your reading. Always use the bathroom first.
Step 3: The “Support” Setup
Sit in a comfortable chair (a dining chair is better than a soft sofa).
- Feet: Keep both feet flat on the floor. Never cross your legs. Crossing your legs cuts off circulation slightly and creates resistance, raising the reading.
- Back: Your back should be supported straight against the chair. Slouching can affect blood flow.
Step 4: The Heart-Level Position
Rest your arm on a table or flat surface.
- The Goal: The cuff on your upper arm should be at the same height as your heart.
- Why? If your arm is dangling down at your side, gravity makes the blood pressure read higher. If it is held up too high, it reads lower.
Step 5: The “Two-Finger” Test
Wrap the cuff around your bare skin (not over a sweater). It should be snug, but not painful.
- The Check: You should be able to slide just two fingertips under the top edge of the cuff. If you can fit your whole hand, it is too loose. If you can’t fit a finger, it is too tight.
Step 6: The Golden Silence
Once the cuff starts inflating, do not talk.
- Talking requires effort and changes your breathing pattern. Even active listening (nodding while someone talks to you) can raise your number by 10 points. Sit in absolute silence.
Step 7: The “Rule of Three”
One reading is just a snapshot. For the truth, you need an average.
- Take one reading.
- Wait 1 minute.
- Take a second reading.
- (Optional but recommended) Take a third.
- The Result: Average the last two readings together. This is your true blood pressure.
Safety Precautions: When to Call a Doctor

Seeing a high number on the screen can be scary. Your heart starts racing, which only makes the number go higher!
Remember: One high reading does not mean you are in immediate danger. Blood pressure fluctuates all day. However, there are specific “Red Zones” where you must act fast.
1. Warning Signs of a Hypertensive Crisis
A “Hypertensive Crisis” is when your blood pressure spikes to dangerous levels, potentially risking a stroke or heart attack.
- The Number: If your reading is 180/120 mmHg or higher.
- The Protocol:
- Don’t Panic. Sit quietly for 5 minutes.
- Retest. Take the blood pressure again.
- If it is still high: Look for symptoms.
The Symptoms:
- Severe chest pain.
- Severe headache, accompanied by confusion or blurred vision.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Shortness of breath.
- Seizures or unresponsiveness.
Action: If you have a high number AND any of these symptoms, call 911 immediately. Do not drive yourself to the hospital.
2. The Hidden Risk: Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
We talk so much about high blood pressure that we forget low blood pressure can be dangerous too, especially for seniors.
- The Number: Generally below 90/60 mmHg.
- The Risk: Low pressure means your brain isn’t getting enough blood quickly enough. This causes dizziness, fainting, and falls. For an older adult, a fall can lead to broken hips or serious injury.
- Action: If you feel lightheaded when standing up, talk to your doctor. They may need to lower your medication dosage.
3 Simple Ways to Start Lowering Numbers Today
If your reading fell into the “Elevated” or “High” category on our chart, take a deep breath. This is not a life sentence. It is a wake-up call. You can often lower your numbers significantly just by changing your daily habits. Here are three proven places to start:
1. Shake the Salt Habit (The Sponge Effect)
Sodium acts like a sponge. It holds onto water in your body. The more water you hold, the higher the pressure in your pipes.
- Quick Fix: Stop adding table salt to meals instead flavor with lemon juice, garlic, or herbs.
2. The 30-Minute Walk
You don’t need to run a marathon. Walking for just 30 minutes a day helps your heart become more efficient. A strong heart pumps blood with less effort, which lowers the pressure on your arteries.
3. Breathe Away the Stress
Stress releases hormones that tighten your blood vessels. Spending just 5 minutes doing deep breathing exercises can relax those vessels and drop your pressure instantly.
Want a Complete Plan?: For a detailed guide on what to eat and how to live, read our step-by-step guide on managing blood pressure levels naturally.
Frequently Asked Questions (The Mega-FAQ)
Here are the answers to the most common questions patients ask about their blood pressure numbers.
Conclusion: You Are More Than Just a Number
It is easy to let a number on a screen define your mood. You see a “High” result, and immediately, the worry sets in. Is my heart okay? Do I need medication forever?
As we have learned, a blood pressure reading is not a static grade on a test. It is a dynamic signal from your body. It changes with your age, your stress levels, and even the time of day. A “perfect” score for a 20-year-old is not necessarily the goal for a 70-year-old.
Your 3-Step Action Plan
Now that you have the chart and the knowledge, here is your immediate “To-Do” list to take control of your heart health:
- Find Your Baseline: Don’t rely on one stressful doctor’s visit. Use the 7-Step Ritual to measure your pressure at home for one week.
- Respect Your Age: Understand that stiffening arteries are a part of life, but they don’t have to dictate your future. Small lifestyle tweaks often work better than you think.
- Start Small: You don’t need to overhaul your life overnight. Start by drinking one extra glass of water and taking a 10-minute walk today.
You are in the driver’s seat. Your blood pressure is something you can manage, improve, and master.
- American Heart Association (AHA): Understanding Blood Pressure Readings https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings
- Mayo Clinic: High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Symptoms & Causes https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20373410
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): High Blood Pressure Facts https://www.cdc.gov/bloodpressure/facts.htm
- National Institute on Aging: High Blood Pressure in Older Adults https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/high-blood-pressure/high-blood-pressure-older-adults
- Cleveland Clinic: White Coat Syndrome https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21893-white-coat-syndrome
Trust in your purchase:
Every product featured on our site has been carefully researched and selected based on quality, customer ratings, and positive reviews to ensure you receive excellent value for your money.
Please note:
This post contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support our site and allows us to continue bringing you valuable content. Thank you!
Thank you for your precious time spent with NobleHomeRemedies.
You may also like:
Gastroparesis Diet Handout
Gastroparesis Diet Handout: 2 Top Gastroparesis CookBooks Gastroparesis is a digestive disorder that affects the…
Epsom Salt for Sunburn
Epsom Salt for Sunburn Relief: 2 Soothing Natural Solutions Sunburns are no fun! We’ve all…
Does Sprite Have Caffeine?
Does Sprite Have Caffeine? – How Safe Is It to Drink? The presence of caffeine…
Lower blood pressure naturally
The Ultimate Guide to Lower Blood Pressure Naturally (Without Meds) Medical Disclaimer: The information in…
Can Coffee After Drinking Alcohol Sober You?
Drinking Coffee After Drinking Alcohol: Can It Sober You Up? When people drink alcohol, they…
How to Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI)
How to Calculate Body Mass Index (BMI): Are you obese? The first level of assessment…