Understanding Tooth Infections: Causes, Symptoms & Remedies

A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, is a common oral health issue that can cause discomfort, pain, and other complications if left untreated.
It occurs when bacteria enter the tooth or surrounding tissues, leading to an infection. As such, it’s crucial to understand the causes, symptoms, and remedies associated with tooth infections to manage and prevent further complications effectively.
In this blog post, we will delve into the details of tooth infections, providing valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, and remedies. It will help you better understand this oral health concern and take appropriate action. Let’s explore the world of tooth infections and equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to maintain good oral health.
Causes of Tooth Infections
Tooth infections can have various underlying causes. Understanding these causes can help you take steps to prevent them and maintain good oral health. Here are some common causes and types of tooth infections:
Dental decay and cavities: Dental decay, also known as dental caries, occurs when the protective enamel on the tooth’s surface is eroded by bacteria, leading tocavities. If left untreated, cavities can progress deeper into the tooth, reaching the pulp, which can result in tooth infection.
Gum disease and periodontal abscess: Gum disease, also known as gingivitis, is an inflammation of the gums caused by the accumulation of plaque and bacteria along the gumline. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, which involves the destruction of gum tissue and bone supporting the teeth. This can create pockets where bacteria can thrive, leading to tooth infections.
Trauma or injury to the tooth: Trauma or injury to the tooth, such as a crack or fracture, can create an entry point for bacteria to enter the tooth, leading to an infection. Accidents, sports injuries, or even biting down on hard objects can cause such trauma or injury to the tooth.
Failed dental procedures: Sometimes, dental procedures like fillings, crowns, or root canals may fail to completely eliminate bacteria from the tooth, leading to persistent or recurrent infections. It’s essential to follow up with your dentist if you experience persistent discomfort or pain after a dental procedure.
Poor oral hygiene habits: Neglecting regular brushing, flossing, and maintaining proper oral hygiene habits can allow plaque and bacteria to accumulate on the teeth and gums. This can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and ultimately, tooth infections.
Understanding these common causes of tooth infections can help you take preventive measures, such as maintaining good oral hygiene practices, seeking timely dental care, and being cautious of potential tooth trauma. By addressing these causes, you can reduce the risk of tooth infections and maintain optimal oral health.
Symptoms of Tooth Infections
Tooth infections can manifest through various symptoms that may vary in severity depending on the extent of the infection. Recognizing these symptoms can help you identify a tooth infection and seek prompt dental care. Here are some common symptoms of tooth infections:
Tooth pain, sensitivity, and throbbing: Tooth infections often cause localized pain, sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages, and throbbing sensations in the affected tooth. The pain may worsen when you bite or chew.
Swelling and redness in the gums: Inflammation and swelling of the gums around the infected tooth are common symptoms of a tooth infection. The gums may appear red, swollen, and tender to the touch.
Bad breath and a foul taste in the mouth: Tooth infections can lead to the release of bacteria-produced toxins that can cause bad breath (halitosis) and a foul taste in the mouth that persists even after brushing or using mouthwash.
Difficulty chewing or biting: Tooth infections can affect the functionality of the affected tooth, making it difficult to chew or bite down properly. This may result in discomfort while eating or drinking.
Fever and general discomfort: In some cases, tooth infections can cause systemic symptoms such as fever, general discomfort, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw area.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek prompt dental care from a qualified dentist to properly diagnose and treat the tooth infection. Delaying treatment can lead to further complications and the potential symptoms of tooth infection spreading to the body. Proper identification and timely intervention can help prevent further discomfort and promote optimal oral health.
Diagnosing Tooth Infections
Properly diagnosing a tooth infection is crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. Dentists and dental professionals use various methods to diagnose tooth infections, including:
Dental examination and X-rays: During a dental examination, the dentist will visually inspect the affected tooth and surrounding tissues for signs of infection, such as swelling, redness, and pus. X-rays may also be taken to get a clearer picture of the tooth’s internal structure and identify any hidden signs of infection, such as abscesses or bone loss.
Evaluation of symptoms and medical history: The dentist will carefully evaluate the patient’s reported symptoms, including tooth pain, sensitivity, swelling, and other related issues. The patient’s medical history, including any previous dental procedures or treatments, may also be taken into consideration to gain a comprehensive understanding of the potential causes of the tooth infection.
Consulting with a dentist or dental professional
Dentists and dental professionals are highly trained and experienced in diagnosing tooth infections. If you suspect a tooth infection, it’s essential to consult with a qualified dentist or dental professional for an accurate diagnosis. They may use a combination of clinical examination, X-rays, and other diagnostic tools to determine the underlying cause and severity of the infection.
Proper and timely diagnosis of a tooth infection is crucial for effective treatment planning. If you suspect a tooth infection, it’s important not to self-diagnose or delay seeking professional dental care. A dentist or dental professional can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific condition, helping you achieve optimal oral health and prevent potential complications.
Remedies for Tooth Infections
Tooth infections require prompt and appropriate treatment to prevent further complications and alleviate discomfort. Depending on the severity of the infection, various remedies may be recommended, including:
Antibiotics and prescribed medications: In cases of mild to moderate tooth infections, antibiotics may be prescribed by a dentist or dental professional to help eliminate the infection and prevent its spread. It’s essential to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of the medication for effective results.
Natural tooth infection, antibiotics, and home remedies for alleviating symptoms: In addition to professional dental care, there are some home remedies and natural antibiotics that may help alleviate symptoms of tooth infections. These include rinsing the mouth with warm salt water, applying a cold compress to the affected area to reduce swelling, avoiding hot or cold foods and drinks, and maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly.
Root canal treatment: If the tooth infection has reached the inner pulp of the tooth, a root canal treatment may be recommended. This involves removing the infected pulp and filling the tooth to prevent further infection and restore its function. Root canal treatment is typically performed by a qualified dentist or endodontist and can save the tooth from extraction in many cases.
Tooth extraction in severe cases: In severe cases where the tooth is extensively damaged or the infection cannot be effectively treated with antibiotics or root canal treatment, tooth extraction may be necessary. Tooth extraction involves removing the infected tooth to prevent the spread of infection to other teeth or areas of the mouth.
Pain management techniques: Tooth infections can be extremely painful, and pain management techniques may be recommended to alleviate discomfort. This can include over-the-counter pain medications, numbing gels, or prescribed pain relief medications as advised by a dentist or dental professional.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices: Good oral hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing and managing tooth infections. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and visiting your dentist regularly for dental cleanings and check-ups. Maintaining proper oral hygiene can help prevent dental decay, gum disease, and other conditions that can lead to tooth infections.
It’s important to note that the appropriate remedy for a tooth infection depends on the severity of the infection and the recommendation of a qualified dentist or dental professional. If you suspect a tooth infection, it’s crucial to seek professional dental care promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent potential complications and maintain optimal oral health.
Prevention of Tooth Infections
Tooth infections can be prevented with proper oral care and healthy habits. By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of tooth infections:
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings: Visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings is crucial in preventing tooth infections. Your dentist can detect any early signs of dental issues and provide appropriate treatments to prevent the progression of infections.
Brushing and flossing daily: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily helps remove plaque and bacteria that can lead to dental decay and gum disease. Proper brushing and flossing techniques can effectively prevent tooth infections by maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
Limiting sugar and acidic foods: Consuming excessive sugar and acidic foods can contribute to dental decay, which can lead to tooth infections. Limiting your intake of sugary foods and beverages, as well as acidic foods, can help prevent tooth infections by reducing the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Avoiding tobacco and alcohol: Tobacco and alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on oral health, including an increased risk of tooth infections. Quitting smoking or tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of tooth infections and promote overall oral health.
Protecting teeth from trauma or injury: Trauma or injury to the teeth can also increase the risk of tooth infections. Taking precautions to protect your teeth during physical activities or sports, wearing a mouthguard if necessary, and avoiding using your teeth to open packages or bite on hard objects can help prevent tooth infections caused by trauma or injury.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine and seeking professional dental care regularly, you can effectively reduce the risk of tooth infections and maintain optimal oral health. Prevention is always better than cure, and taking proactive steps to prevent tooth infections is crucial in maintaining a healthy and infection-free mouth.
Takeaway
Understanding tooth infections, including their causes, symptoms, and remedies, is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. Dental decay and cavities, gum disease, trauma to the tooth, failed dental procedures, and poor oral hygiene habits are common causes of tooth infections.
Symptoms such as tooth pain, swelling, bad breath, difficulty chewing, and fever may indicate a tooth infection. Remedies for tooth infections may include antibiotics, root canal treatment, tooth extraction in severe cases, pain management techniques, and maintaining good oral hygiene practices.
However, it’s important to seek professional dental care if you suspect a tooth infection. Dentists and dental professionals are trained to diagnose and treat tooth infections effectively. Early detection and prompt treatment can prevent the spread of infection and potential complications.
In addition, maintaining good oral health practices on a daily basis can help prevent tooth infections in the first place. Brushing and flossing regularly, limiting sugar and acidic foods, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, protecting teeth from trauma, and scheduling regular dental check-ups and cleanings are crucial preventive measures.
Finally, seeking professional dental care, along with practicing good oral hygiene habits, can help prevent tooth infections and ensure a healthy and infection-free mouth. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, so take proactive steps to protect your teeth and maintain good oral health practices for a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Trust in your purchase:
Every product featured on our site has been carefully researched and selected based on quality, customer ratings, and positive reviews to ensure you receive excellent value for your money.
Please note:
This post contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. This helps support our site and allows us to continue bringing you valuable content. Thank you!
Thank you for your precious time spent with NobleHomeRemedies.
You may also like:
Teeth Whitening At Home
Brighten Your Smile: The Ultimate Guide to Teeth Whitening at Home Embarking on a journey…
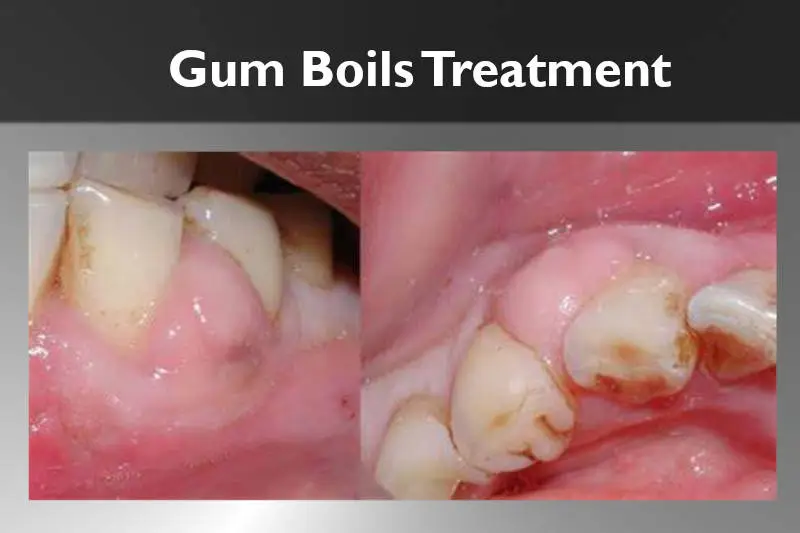
Gum Boils Treatment
Gum Boils Treatment: The Powerful Solution You Need! Welcome to our blog post on gum…
Fast Tooth Pain Relief Natural Remedies
Fast Tooth Pain Relief Natural Remedies – Pepper & Salt Toothache pain can be controlled….
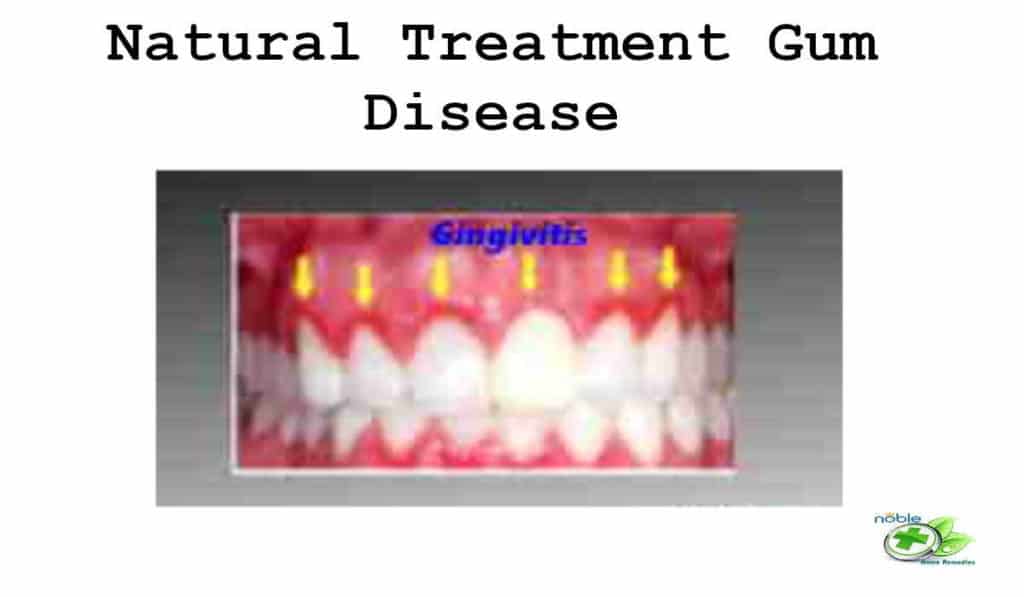
Top 7 Natural Treatment Gum Disease
Top 7 Natural Treatment Gum Disease Gum disease is an infection of tissues of the…
Activated Charcoal Teeth Whitening
Truth About Activated Charcoal Teeth Whitening: Abrasive? The black magic of activated charcoal is a…
How to Remove Stains from Teeth Naturally
How to Remove Stains from Teeth in Just One Day?: Naturally! How to remove stains…